Welcome to the Plus Two Biology Answer Key 2025! This Post is designed to help students check their answers and understand key concepts easily. The solutions provided are accurate and follow the latest exam pattern.
Biology is an exciting subject that teaches us about life and the world around us. This answer key will help you review your responses, learn from mistakes, and improve your understanding. Whether you are preparing for exams or just revising, this resource will be a valuable tool.
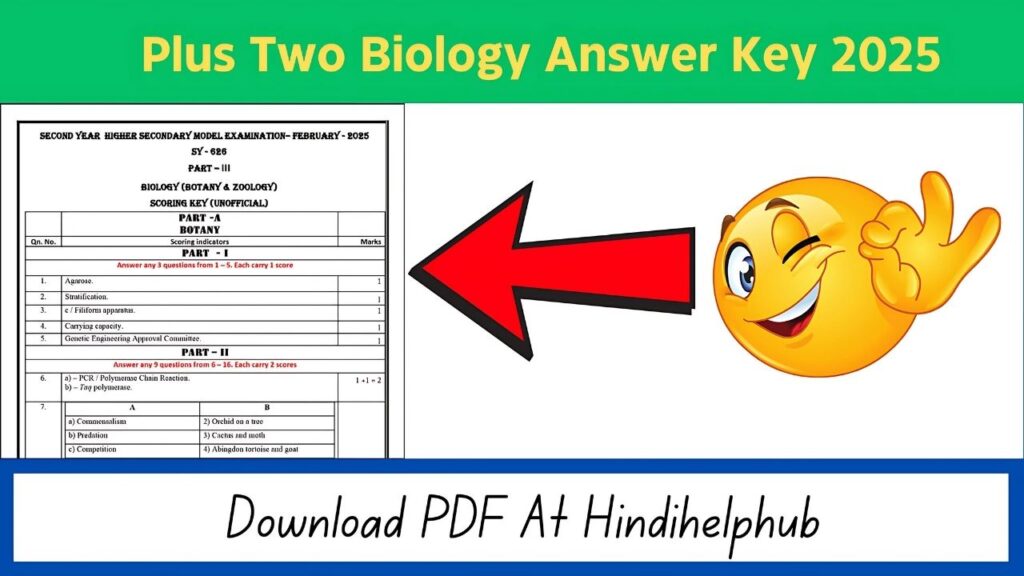
Plus Two Biology Answer Key 2025
SECOND YEAR HIGHER SECONDARY MODEL EXAMINATION – FEBRUARY 2025 SY – 626
PART – II
BIOLOGY (BOTANY & ZOOLOGY)
SCORING KEY (UNOFFICIAL)
PART – A: BOTANY
Qn.No. | Scoring Indicators | Marks
- Filiform apparatus.
Genetic Engineering Approval Committee.
a) PCR / Polymerase Chain Reaction. (1+1=2)
b) Taq polymerase. - Predation
- Cactus and moth
Energy at a lower trophic level is always more than at a higher level. Energy flow from one trophic level to the next level loses some energy as heat at each step. It follows the law of 10% (only 10% of the energy is transferred to each trophic level). (1+1=2)
Any 1 point gives full score. - X – Proinsulin
Y – Insulin / A Peptide (1+1=2)
C – Peptide - Bt toxin protein is produced as an inactive protoxin in bacterial cells, so it does not kill the bacteria themselves.
- Leaching, Catabolism, Humification, Mineralisation. (2×4=2)
- a) Origin of replication (ori) / Selectable markers / Cloning sites (Any two)
- Food Chain Differences(1+1=2)
- Starts with producers/green plants in an aquatic ecosystem.
- Starts with detritus/dead organic matter in a terrestrial ecosystem.
- Producers (plants) belong to the first trophic level.
- Dead organic matter belongs to the first trophic level.
Any one point in each.
- a) A – Mortality (D)
b) Natality and Immigration (I & B) - True Fruit – Fruit developed from the ovary (Eg: Mango, Coconut, Pea)
False Fruit – Fruit developed from the thalamus / flower parts other than the ovary (Eg: Apple, Cashew, Strawberry) (1+1=2)
Examples for each type give half score. - Examples of Hydrophytes: Vallisneria, Hydrilla, Zostera (Any one example)
Adaptations: Pollen grains are long, ribbon-like and carried passively inside the water. Pollen grains are protected from wetting by a mucilaginous covering. Female flowers have a long stalk. In Vallisneria, pollen grains are released into the surface of the water and carried to the stigma by air currents. In sea grass, flowers remain submerged. (Any three features – 1+1+1=3)
PART – B: ZOOLOGY
Qn.No. | Scoring Indicators | Marks
- IMR – Infant Mortality Rate
MMR – Maternal Mortality Rate (1 mark) - ABO Blood Group in Humans
- a) LH surge → Ovulation
b) Leydig cells → Secrete androgens
c) Ampullary region → Site of fertilization
d) Sertoli cells → Provide nutrition to spermatids (1+1=2) - a) Symbiotic associations between fungi and roots of higher plants.
b) Fungal symbiont absorbs phosphorus from soil and passes it to the plant, develops resistance to root-borne pathogens, tolerance to salinity/drought, and enhances plant growth. (Any one benefit – 1+1=2) - a) Theory of Chemical Evolution / Oparin-Haldane Theory
b) CH4, NH3, H2O, H2 (1+1=2) - a) One parental DNA strand is conserved in the newly formed DNA molecule after replication. The newly synthesized DNA molecule has one parental and one newly synthesized strand.
b) DNA-dependent DNA polymerase / DNA Polymerase.
c) S-phase. (1+1=2) - a) A – Citric Acid
b) B – Trichoderma polysporum
c) C – Lactic Acid
d) D – Monascus purpureus (1+1=2) - a) Adaptive Radiation: The process of evolution of different species in a given geographical area starting from a point and radiating to other areas/habitats. (1+1=2)
- Difference Between Homologous & Analogous Organs:
- Homologous Organs: Similar structure, different function; indicate common ancestry (Eg: Forelimbs of whale, bat, human, cheetah).
- Analogous Organs: Similar function, different structure; represent convergent evolution (Eg: Wings of butterfly and birds, flippers of penguins and dolphins). (Any one difference & example – 1+1=2)
- a) Cu-T
b) Copper ions suppress sperm motility and fertilizing capacity of sperms / Increase phagocytosis of sperms. (1+1=2) - a) Pregnancy
b) Placenta
c) Human Placental Lactogen (hPL) / Estrogen / Progesterone (Any two) (1+1=2) - a) Nucleosome
b) Histone Octamer
c) Euchromatin vs. Heterochromatin:- Euchromatin: Loosely packed, light stainable, transcriptionally active.
- Heterochromatin: Densely packed, dark stainable, transcriptionally inactive. (Any two differences – 1+1=2)
- a) Hardy-Weinberg Principle / Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium.
b) Factors: Gene flow, Genetic drift, Mutation, Genetic recombination, Natural selection (Any two – 1+1=2). - a) ZIFT – Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer (Zygote/Early embryo up to 8 blastomeres transferred into fallopian tube).
b) IUT – Intra Uterine Transfer (Embryo >8 blastomeres transferred into uterus). (1+2=3) - a) Alec Jeffreys
b) VNTR – Variable Number of Tandem Repeats
c) Used in forensic studies, evolutionary biology, genetic biodiversity studies, parental disputes (Any two – 1+2=3).
Prepared by: Dr. SUNIL KUMAR. S
NVT Biology, GFVHSS Cheruvathur
Plus Two Biology Answer Key 2025 Pdf – Download